Since m 1 then m 2 m. Ad Enjoy low prices on earths biggest selection of books electronics home apparel more.

Economies Of Scale How To Scale The Right Way
Economies of scale is the concept suggesting that a business receives an advantage in cost per product produced as its output of the product increases.
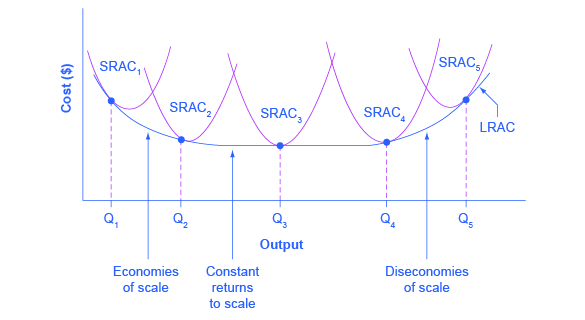
. Economies of Scale A small factory like S produces 1000 alarm clocks at an average cost of 12 per clock. It takes place when economies of scale no longer function for a firm. So as you get more and more scale you can have different parts of your process specializing in making the taco shells or grating the cheese or cooking the meat.
Read customer reviews find best sellers. At the basis of economies of scale there may be technical statistical organizational or related factors to the. Economies of scale are cost advantages reaped by companies when production becomes efficient.
This means that the unit cost of production remains constant as the scale of production increases. A medium factory like M produces 2000 alarm clocks at a cost of 8 per clock. Our new production has increased by more than m so we have increasing returns to scale.
The LRAC of the firm keeps falling with the increase in the production of units. Means that it needs the double amount of all production factor inputs ie. It can come from specialization of labor or even machines.
In most perfectly competitive models it is assumed that production takes place with constant returns to scale ie no economies. And weve talked about where economies of scale can come from. This may arise as a result of buying the inputs in large quantities which lowers the cost per unit.
And so at this part of our curve we are experiencing economies of scale. Lets examine the difference between constant returns to scale and economies of scale. Constant economies of scale.
A decrease in cost per unit of output enables an increase in scale. In microeconomics economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation and are typically measured by the amount of output produced per unit of time. Constant economies of scale describe a situation in which an increase in produced units leads to no change in the ratio of input and output.
When companies achieve constant returns to scale in their production efforts they can know to stop adding additional inputs because theyve achieved a healthy relationship between their invested resources and. Companies can achieve economies of scale by increasing production and lowering costs. If an input increases by 20 the output will also increase by 20.
Define Constant economies of scale. Each single input however yields decreasing partial returns to scale ie. With this principle rather than experiencing continued decreasing costs and increasing output a firm sees an increase in.
Browse discover thousands of brands. Constant positive and negative economies of scale. Q 5KmLm 5KLm 2 Q m 2.
Again we increase both K and L by m and create a new production function. This occurs because the per-item production. At this stage the LRAC remains static with the increase in.
Constant returns to scale refer to the output reflected in equal proportion to the input. Goolsbee Levitt Syverson 2016 Microeconomics Worth Publishers. When a company has a constant return to scale it may benefit from economies of scale.
2 Constant Returns of Scale The constant return of scale is a state where the firm begins to start entering the maturity stage. Total cost rises at the same rate as output rises. When that assumption is changed it can open up the possibility of positive profits and strategic behavior among firms.
And at the same time has increasing or constant economies of scale when all inputs change together to produce a larger-scale operation. The more one increases the input of one single factor while leaving the other inputs constant the less is this factors marginal return. Finally the right.
The same case goes for a decrease in production. This means that as businesses increase in size they can lower their production costs and create a competitive advantage by either using those cost savings for increased profits or using the savings to. There are three types of economies of scale.
Economies of scale are a reduction in costs to a business which occur when the company increases the production of their goods and becomes more efficient. Labour and capital to exactly double the output produced. Let us say the company always needs 5 input units.
As a result we have constant returns to scale. Economies of scale refers to the long-run average cost curve where all inputs are being allowed to increase together. 1 Economies of Scale It is a state where the firm experiences the highest operational efficiency.
Thus it is quite possible and common to have an industry that has both diminishing marginal returns when only one input is allowed to change and at the same time has increasing or constant economies of scale when all inputs change together to produce a larger. A constant return to scale likely means your company is appropriately employing inputs and producing large quantities of products at low costs. For example a company uses A as an input and produces B as an output.
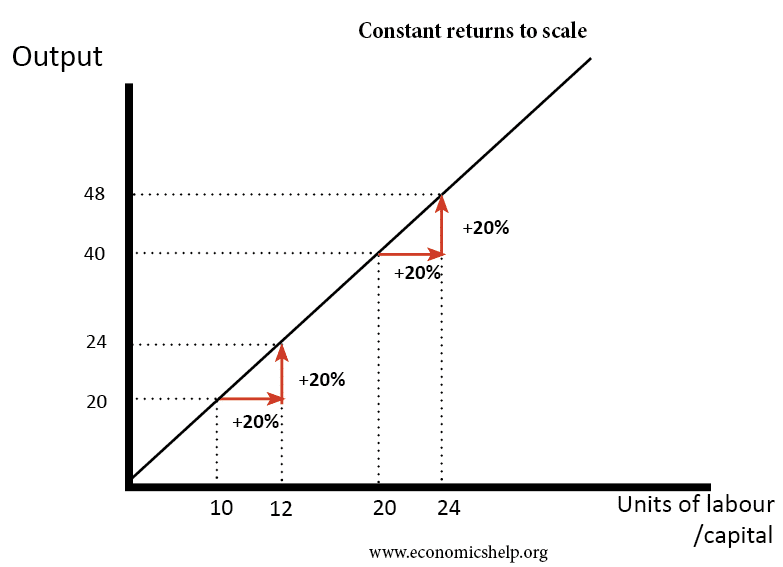
Constant Returns To Scale Economics Help
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/MinimumEfficientScaleMES2-c9372fffba0a4a1ab4ab0175600afdb6.png)
Minimum Efficient Scale Mes Definition

0 Comments